Frequently Asked Questions
Deseq2
The tutorial uses the normalised count table for visualisation. What about using VST normalised counts or rlog normalised counts?
The tutorial uses the normalised count table for visualisation. What about using VST normalised counts or rlog normalised counts?
this depends on what you would like to do with the table. The DESeq2 wrapper in Galaxy can output all of these, and there is a nice discussion in the DESeq2 vignette about this topic.
Estimation of strandedness
When is the "infer experiment" tool used in practice?
When is the “infer experiment” tool used in practice?
Often you are already aware whether the RNA-seq data is stranded or not in the first place because you sequenced it yourself or ordered it from a company.
But it can happen in cases where you get the data from someone else, that this information is lost and you need to find out.
In 'infer experiments' I get unequal numbers, but in the IGV it looks like it is unstranded. What does this mean?
In ‘infer experiments’ I get unequal numbers, but in the IGV it looks like it is unstranded. What does this mean?
It’s also often the case that elimination of the second strand is not perfect, and there are genuine cases of bidirectional transcription in the genome. 70 / 30 % as in your report is not a good result for a stranded library. You can treat this as a stranded library in your analysis, but for instance you couldn’t make the conclusion that a given gene is actually transcribed from the reverse strand. Likely that the library preparation didn’t work perfectly. This can depend on many factors, one is that you need to completely digest your DNA using a high quality DNase before doing the reverse transcription.
Mapping
Is it possible to visualize the RNA STAR bam file using the JBrowse tool?
Is it possible to visualize the RNA STAR bam file using the JBrowse tool?
Yes, that should work.
RNAstar: Why do we set 36 for 'Length of the genomic sequence around annotated junctions'?
RNAstar: Why do we set 36 for ‘Length of the genomic sequence around annotated junctions’?
RNA STAR is using the gene model to create the database of splice junctions, and that these don’t “need” to have a length longer than the reads (37bp).
Visualisation
Using IGV with Galaxy
Tip: Using IGV with Galaxy
You can send data from your Galaxy history to IGV for viewing as follows:
- Install IGV on your computer (IGV download page)
- Start IGV
- In recent versions of IGV, you will have to enable the port:
- In IGV, go to
View > Preferences > Advanced- Check the box
Enable Port- In Galaxy, expand the dataset you would like to view in IGV
- Make sure you have set a reference genome/database correctly (dbkey) (instructions)
- Under
display in IGV, click onlocal
General Questions
Can't find one of the tools for this tutorial?
Tip: If a Tool is Missing
To use the tools installed and available on the Galaxy server:
- At the top of the left tool panel, type in a tool name or datatype into the tool search box.
- Shorter keywords find more choices.
- Tools can also be directly browsed by category in the tool panel.
If you can’t find a tool you need for a tutorial on Galaxy, please:
- Check that you are using a compatible Galaxy server
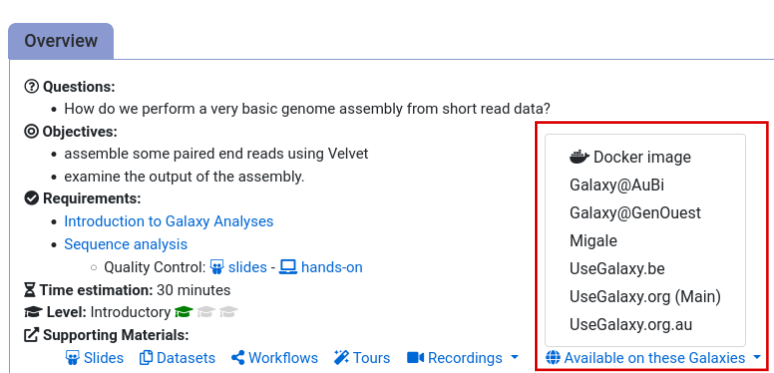
- Navigate to the overview box at the top of the tutorial
- Find the “Supporting Materials” section
- Check “Available on these Galaxies”
- If your server is not listed here, the tutorial is not supported on your Galaxy server
- You can create an account on one of the supporting Galaxies
- Use the Tutorial mode feature
- Open your Galaxy server
- Click on the curriculum icon on the top menu, this will open the GTN inside Galaxy.
- Navigate to your tutorial
- Tool names in tutorials will be blue buttons that open the correct tool for you
- Note: this does not work for all tutorials (yet)
- Still not finding the tool?
- Ask help in Gitter.
Running into an error?
Tip: Troubleshooting errors
When something goes wrong in Galaxy, there are a number of things you can do to find out what it was. Error messages can help you figure out whether it was a problem with one of the settings of the tool, or with the input data, or maybe there is a bug in the tool itself and the problem should be reported. Below are the steps you can follow to troubleshoot your Galaxy errors.
- Expand the red history dataset by clicking on it.
- Sometimes you can already see an error message here
View the error message by clicking on the bug icon galaxy-bug
- Check the logs. Output (stdout) and error logs (stderr) of the tool are available:
- Expand the history item
- Click on the details icon
- Scroll down to the Job Information section to view the 2 logs:
- Tool Standard Output
- Tool Standard Error
- Submit a bug report! If you are still unsure what the problem is.
- Click on the bug icon galaxy-bug
- Write down any information you think might help solve the problem
- See this FAQ on how to write good bug reports
- Click galaxy-bug Report button
- Ask for help!
- Where?
- In the GTN Gitter Channel
- In the Galaxy Gitter Channel
- Browse the Galaxy Help Forum to see if others have encountered the same problem before (or post your question).
- When asking for help, it is useful to share a link to your history