Functional annotation of protein sequences
| Author(s) |
 |
Overview
Questions:Objectives:
How to perform functional annotation on protein sequences?
Requirements:
Perform functional annotation using EggNOG-mapper and InterProScan
Time estimation: 1 hourLevel: Introductory IntroductorySupporting Materials:Last modification: Jul 20, 2022
Introduction
When performing the structural annotation of a genome sequence, you get the position of each gene, but you don’t have information about their name of their function. That’s the goal of functional annotation.
In this short tutorial, we will run the most commonly used tools to perform functional annotation, starting from the predicted protein sequences of a few example genes.
For a more complete view of how this step integrates into a whole genome sequencing and annotation process, you can have a look at the Funannotate tutorial.
Agenda
In this tutorial, we will cover:
Data upload
We will annotate a small set of protein sequences. These sequences were predicted from the gene structures obtained in the Funannotate tutorial? Though these sequences from from a fungal species, you can run the same tools on proteins from any organisms, including prokaryotes.
hands_on Hands-on: Data upload
Create a new history for this tutorial
Tip: Creating a new history
Click the new-history icon at the top of the history panel.
If the new-history is missing:
- Click on the galaxy-gear icon (History options) on the top of the history panel
- Select the option Create New from the menu
Import the files from Zenodo or from the shared data library (
GTN - Material->genome-annotation->Functional annotation of protein sequences):https://zenodo.org/api/files/6628a5e4-d6be-47bd-bdaa-f2646112578e/proteins.fastaTip: Importing via links
- Copy the link location
Open the Galaxy Upload Manager (galaxy-upload on the top-right of the tool panel)
- Select Paste/Fetch Data
Paste the link into the text field
Press Start
- Close the window
Tip: Importing data from a data library
As an alternative to uploading the data from a URL or your computer, the files may also have been made available from a shared data library:
- Go into Shared data (top panel) then Data libraries
- Navigate to the correct folder as indicated by your instructor
- Select the desired files
- Click on the To History button near the top and select as Datasets from the dropdown menu
- In the pop-up window, select the history you want to import the files to (or create a new one)
- Click on Import
Functional annotation
EggNOG Mapper
EggNOG Mapper compares each protein sequence of the annotation to a huge set of ortholog groups from the EggNOG database. In this database, each ortholog group is associated with functional annotation like Gene Ontology (GO) terms or KEGG pathways. When the protein sequence of a new gene is found to be very similar to one of these ortholog groups, the corresponding functional annotation is transfered to this new gene.
hands_on Hands-on
- eggNOG Mapper Tool: toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/galaxyp/eggnog_mapper/eggnog_mapper/2.1.8+galaxy2.1.8 with the following parameters:
- param-file “Fasta sequences to annotate”:
proteins.fasta(Input dataset)- “Version of eggNOG Database”: select the latest version available
- In “Output Options”:
- “Exclude header lines and stats from output files”:
No
The output of this tool is a tabular file, where each line represents a gene from our annotation, with the functional annotation that was found by EggNOG-mapper. It includes a predicted protein name, GO terms, EC numbers, KEGG identifiers, …
Display the file and explore which kind of identifiers were found by EggNOG Mapper.
InterProScan
InterPro is a huge integrated database of protein families. Each family is characterized by one or muliple signatures (i.e. sequence motifs) that are specific to the protein family, and corresponding functional annotation like protein names or Gene Ontology (GO). A good proportion of the signatures are manually curated, which means they are of very good quality.
InterProScan is a tool that analyses each protein sequence from our annotation to determine if they contain one or several of the signatures from InterPro. When a protein contains a known signature, the corresponding functional annotation will be assigned to it by InterProScan.
InterProScan itself runs multiple applications to search for the signatures in the protein sequences. It is possible to select exactly which ones we want to use when launching the analysis (by default all will be run).
hands_on Hands-on
- InterProScan Tool: toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/bgruening/interproscan/interproscan/5.55-88.0+galaxy3 with the following parameters:
- param-file “Protein FASTA File”:
proteins.fasta(Input dataset)- “InterProScan database”: select the latest version available
- “Use applications with restricted license, only for non-commercial use?”:
Yes(set it toNoif you run InterProScan for commercial use)- “Output format”:
Tab-separated values format (TSV)andXML
comment Comments
To speed up the processing by InterProScan during this tutorial, you can disable
PfamandPANTHERapplications. When analysing real data, it is adviced to keep them enabled.When some applications are disabled, you will of course miss the corresponding results in the output of InterProScan.
The output of this tool is both a tabular file and an XML file. Both contain the same information, but the tabular one is more readable for a Human: each line represents a gene from our annotation, with the different domains and motifs that were found by InterProScan.
If you display the TSV file you should see something like this:
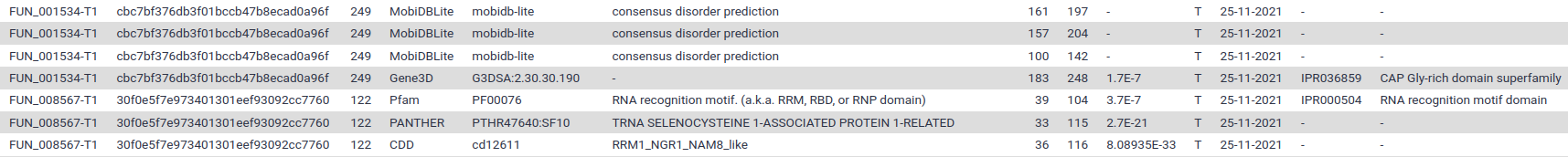
Each line correspond to a motif found in one of the annotated proteins. The most interesting columns are:
- Column 1: the protein identifier
- Column 5: the identifier of the signature that was found in the protein sequence
- Column 4: the databank where this signature comes from (InterProScan regroups several motifs databanks)
- Column 6: the human readable description of the motif
- Columns 7 and 8: the position where the motif was found
- Column 9: a score for the match (if available)
- Column 12 and 13: identifier of the signature integrated in InterPro (if available). Have a look an example webpage for IPR036859 on InterPro.
- The following columns contains various identifiers that were assigned to the protein based on the match with the signature (Gene ontology term, Reactome, …)
The XML output file contains the same information in a computer-friendly format, we will use it in the next step.
Conclusion
Congratulations for reaching the end of this tutorial! Now you know how to perform the functional annotation of a set of protein sequences, using EggNOG mapper and InterProScan.
If you want to collect more functional annotation, you can try to run the NCBI BLAST+ blastp Tool: toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/ncbi_blast_plus/ncbi_blastp_wrapper/2.10.1+galaxy2 or Diamond Tool: toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/bgruening/diamond/bg_diamond/2.0.15+galaxy0 tools against the UniProt or NR databases (Diamond runs much faster on big datasets). These tools will search for similarities between your protein sequences and the ones already described in big international databases.
Also note that many other more specialised tools exist to collect even more functional annotation, in particular for certain species (prokaryotes forexample), or enzyme/protein families.
Key points
EggNOG Mapper compares sequences to a database of annotated orthologous sequences
InterProScan detects known motifs in protein sequences
Frequently Asked Questions
Have questions about this tutorial? Check out the tutorial FAQ page or the FAQ page for the Genome Annotation topic to see if your question is listed there. If not, please ask your question on the GTN Gitter Channel or the Galaxy Help ForumFeedback
Did you use this material as an instructor? Feel free to give us feedback on how it went.
Did you use this material as a learner or student? Click the form below to leave feedback.
Citing this Tutorial
- , 2022 Functional annotation of protein sequences (Galaxy Training Materials). https://training.galaxyproject.org/training-material/topics/genome-annotation/tutorials/functional/tutorial.html Online; accessed TODAY
- Batut et al., 2018 Community-Driven Data Analysis Training for Biology Cell Systems 10.1016/j.cels.2018.05.012
details BibTeX
@misc{genome-annotation-functional, author = "", title = "Functional annotation of protein sequences (Galaxy Training Materials)", year = "2022", month = "07", day = "20" url = "\url{https://training.galaxyproject.org/training-material/topics/genome-annotation/tutorials/functional/tutorial.html}", note = "[Online; accessed TODAY]" } @article{Batut_2018, doi = {10.1016/j.cels.2018.05.012}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.cels.2018.05.012}, year = 2018, month = {jun}, publisher = {Elsevier {BV}}, volume = {6}, number = {6}, pages = {752--758.e1}, author = {B{\'{e}}r{\'{e}}nice Batut and Saskia Hiltemann and Andrea Bagnacani and Dannon Baker and Vivek Bhardwaj and Clemens Blank and Anthony Bretaudeau and Loraine Brillet-Gu{\'{e}}guen and Martin {\v{C}}ech and John Chilton and Dave Clements and Olivia Doppelt-Azeroual and Anika Erxleben and Mallory Ann Freeberg and Simon Gladman and Youri Hoogstrate and Hans-Rudolf Hotz and Torsten Houwaart and Pratik Jagtap and Delphine Larivi{\`{e}}re and Gildas Le Corguill{\'{e}} and Thomas Manke and Fabien Mareuil and Fidel Ram{\'{\i}}rez and Devon Ryan and Florian Christoph Sigloch and Nicola Soranzo and Joachim Wolff and Pavankumar Videm and Markus Wolfien and Aisanjiang Wubuli and Dilmurat Yusuf and James Taylor and Rolf Backofen and Anton Nekrutenko and Björn Grüning}, title = {Community-Driven Data Analysis Training for Biology}, journal = {Cell Systems} }
Funding
These individuals or organisations provided funding support for the development of this resource
This project (2020-1-NL01-KA203-064717) is funded with the support of the Erasmus+ programme of the European Union. Their funding has supported a large number of tutorials within the GTN across a wide array of topics.

 Questions:
Questions: