Genome annotation with Prokka
Overview
Questions:Objectives:
How can we annotate a bacterial genome?
How can we visualize annotated genomic features?
Requirements:
Load genome into Galaxy
Annotate genome with Prokka
View annotations in JBrowse
Time estimation: 1 hourLevel: Introductory IntroductorySupporting Materials:Last modification: May 28, 2021
Introduction
In this section we will use a software tool called Prokka to annotate a draft genome sequence. Prokka is a “wrapper”; it collects together several pieces of software (from various authors), and so avoids “re-inventing the wheel”.
Prokka finds and annotates features (both protein coding regions and RNA genes, i.e. tRNA, rRNA) present on on a sequence. Note, Prokka uses a two-step process for the annotation of protein coding regions: first, protein coding regions on the genome are identified using Prodigal; second, the function of the encoded protein is predicted by similarity to proteins in one of many protein or protein domain databases. Prokka is a software tool that can be used to annotate bacterial, archaeal and viral genomes quickly, generating standard output files in GenBank, EMBL and gff formats. More information about Prokka can be found here.
Agenda
In this tutorial, we will deal with:
Import the data
Prokka requires assembled contigs.
hands_on Hands-on: Obtaining our data
Make sure you have an empty analysis history. Give it a name.
Tip: Creating a new history
Click the new-history icon at the top of the history panel.
If the new-history is missing:
- Click on the galaxy-gear icon (History options) on the top of the history panel
- Select the option Create New from the menu
Import the following files from Zenodo or from the shared data library
https://zenodo.org/record/1156405/files/contigs.fastaTip: Importing via links
- Copy the link location
Open the Galaxy Upload Manager (galaxy-upload on the top-right of the tool panel)
- Select Paste/Fetch Data
Paste the link into the text field
Press Start
- Close the window
Tip: Importing data from a data library
As an alternative to uploading the data from a URL or your computer, the files may also have been made available from a shared data library:
- Go into Shared data (top panel) then Data libraries
- Navigate to the correct folder as indicated by your instructor
- Select the desired files
- Click on the To History button near the top and select as Datasets from the dropdown menu
- In the pop-up window, select the history you want to import the files to (or create a new one)
- Click on Import
Annotate the genome
Now we will run the tool called Prokka.
hands_on Hands-on: Annotate genome
- Prokka Tool: toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/crs4/prokka/prokka/1.14.5+galaxy0 with the following parameters (leave everything else unchanged)
- param-file “contigs to annotate”:
contigs.fasta
Examine the output
Once Prokka has finished, examine each of its output files.
- The GFF and GBK files contain all of the information about the features annotated (in different formats.)
- The .txt file contains a summary of the number of features annotated.
- The .faa file contains the protein sequences of the genes annotated.
- The .ffn file contains the nucleotide sequences of the genes annotated.
View annotated features in JBrowse
Now that we have annotated the draft genome sequence, we would like to view the sequence in the JBrowse genome viewer. First, we have to make a JBrowse file. Then, we can view it within Galaxy.
hands_on Hands-on: Visualize the annotation
- JBrowse Tool: toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/iuc/jbrowse/jbrowse/1.16.9+galaxy0 with the following parameters
- “Reference genome to display”:
Use a genome from history
- param-file “Select the reference genome”:
fnaoutput of Prokka Tool: toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/crs4/prokka/prokka/1.14.5+galaxy0This sequence will be the reference against which annotations are displayed
- “Produce Standalone Instance”:
Yes- “Genetic Code”:
11: The Bacterial, Archaeal and Plant Plastid CodeClick on
Insert Track GroupWe will now set up one track - each track is a dataset displayed underneath the reference sequence (which is displayed as nucleotides in FASTA format). We will choose to display the annotations (the Prokka.gff file).
- In 1: Track Group
- “Track Category”:
gene annotations- Click on
Insert Annotation Trackand fill it with:
- “Track Type”:
GFF/GFF3/BED Features- param-file “GFF/GFF3/BED Track Data”:
gffoutput of Prokka Tool: toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/crs4/prokka/prokka/1.14.5+galaxy0A new file will be created in your history, this contains the JBrowse interactive visualisation. We will now view its contents and play with it
Inspect the
JBrowse on data XX and data XX - Completefile by clicking on the galaxy-eye (eye) iconThe JBrowse window will appear in the centre Galaxy panel.
- Display all the tracks and practice maneuvering around
- Click on the tick boxes on the left to display the tracks
- Select contig 1 in the drop down box. You can only see one contig displayed at a time.
- Zoom by clicking on the
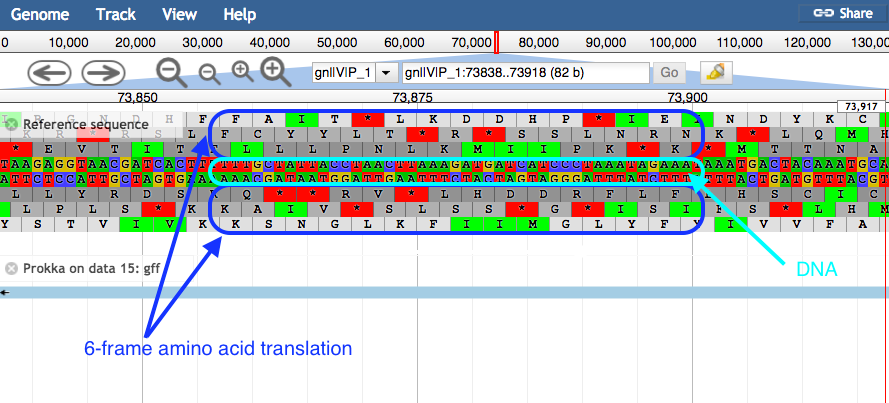
plusandminusbuttons.- JBrowse displays the sequence and a 6-frame amino acid translation.
- Right click on a gene/feature annotation (the bars on the annotation track), then select View Details to see more information.
- gene name
- product name
- you can download the FASTA sequence by clicking on the disk icon
What’s Next
After automatic annotation of prokaryotic genome, if inspection of predicted genes with JBrowse introduced mistakes, e.g. wrong exon/intron limits, splitted genes, or merged genes – or simply if you wish to rename genes or provide additional functional (e.g., Gene Ontology) data, setting up a manual curation project using Apollo helps a lot to manually fix these errors.
The Apollo training should provide additional guidance.
Key points
Prokka is a useful tool to annotate a bacterial genome.
JBrowse can be used to inspect the annotation of a genome.
Frequently Asked Questions
Have questions about this tutorial? Check out the tutorial FAQ page or the FAQ page for the Genome Annotation topic to see if your question is listed there. If not, please ask your question on the GTN Gitter Channel or the Galaxy Help ForumFeedback
Did you use this material as an instructor? Feel free to give us feedback on how it went.
Did you use this material as a learner or student? Click the form below to leave feedback.
Citing this Tutorial
- Anna Syme, Torsten Seemann, Simon Gladman, 2021 Genome annotation with Prokka (Galaxy Training Materials). https://training.galaxyproject.org/training-material/topics/genome-annotation/tutorials/annotation-with-prokka/tutorial.html Online; accessed TODAY
- Batut et al., 2018 Community-Driven Data Analysis Training for Biology Cell Systems 10.1016/j.cels.2018.05.012
details BibTeX
@misc{genome-annotation-annotation-with-prokka, author = "Anna Syme and Torsten Seemann and Simon Gladman", title = "Genome annotation with Prokka (Galaxy Training Materials)", year = "2021", month = "05", day = "28" url = "\url{https://training.galaxyproject.org/training-material/topics/genome-annotation/tutorials/annotation-with-prokka/tutorial.html}", note = "[Online; accessed TODAY]" } @article{Batut_2018, doi = {10.1016/j.cels.2018.05.012}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.cels.2018.05.012}, year = 2018, month = {jun}, publisher = {Elsevier {BV}}, volume = {6}, number = {6}, pages = {752--758.e1}, author = {B{\'{e}}r{\'{e}}nice Batut and Saskia Hiltemann and Andrea Bagnacani and Dannon Baker and Vivek Bhardwaj and Clemens Blank and Anthony Bretaudeau and Loraine Brillet-Gu{\'{e}}guen and Martin {\v{C}}ech and John Chilton and Dave Clements and Olivia Doppelt-Azeroual and Anika Erxleben and Mallory Ann Freeberg and Simon Gladman and Youri Hoogstrate and Hans-Rudolf Hotz and Torsten Houwaart and Pratik Jagtap and Delphine Larivi{\`{e}}re and Gildas Le Corguill{\'{e}} and Thomas Manke and Fabien Mareuil and Fidel Ram{\'{\i}}rez and Devon Ryan and Florian Christoph Sigloch and Nicola Soranzo and Joachim Wolff and Pavankumar Videm and Markus Wolfien and Aisanjiang Wubuli and Dilmurat Yusuf and James Taylor and Rolf Backofen and Anton Nekrutenko and Björn Grüning}, title = {Community-Driven Data Analysis Training for Biology}, journal = {Cell Systems} }
 Questions:
Questions: